Technical Debt Management for DevOps Software Development
Principal Investigator: Dr. Elvira - Maria Arvanitou
Her research interests include technical debt management, software quality metrics, and software maintainability.


My Resume
T2DO Project
Context: In modern software engineering, one of the most important competitive advantages that a company can
demonstrate, is its ability to update a product faster by applying (at as low cost as possible) the new requirements
of the customer, as well as to correct any errors before its reliability in the market is affected.
To ensure the smooth operation (OPeration) of the product, the DevOps development methodology places the customer as a main
stakeholder in the software development process (DEVelopment).
On one hand, the active involvement of customers could lead to less unexpected demands and better control before the delivery
of the product. On the other hand, the active participation of the customers could lead to several design compromises that make
it difficult to maintain the product.
The aforementioned compromises are in the software engieering literature compared with the bank loaning process,
introducing the concept of Technical Debt (Technical Debt--TD). According to CISQ in 2018, the amount of software technical debt in the US was approximately $1.145 trillion, which
represented just the debt principal without accumulated interest. At that time, they assume a code growth rate of 35 billion LOC per year, projecting that there would be 1.455 trillion
LOC worldwide (US share of 31%). Projecting those figures to 2020, and assuming that very little code has since been retired, there would now be 1.655 trillion LOC worldwide and 513 billion
in the US. The US figure for technical debt in 2020 would therefore be $1.31 trillion. Thus, it becomes clear that software engineering companies need methods and tools to manage their
technical debt, as they apply modern software development methodologies, such as DevOps.
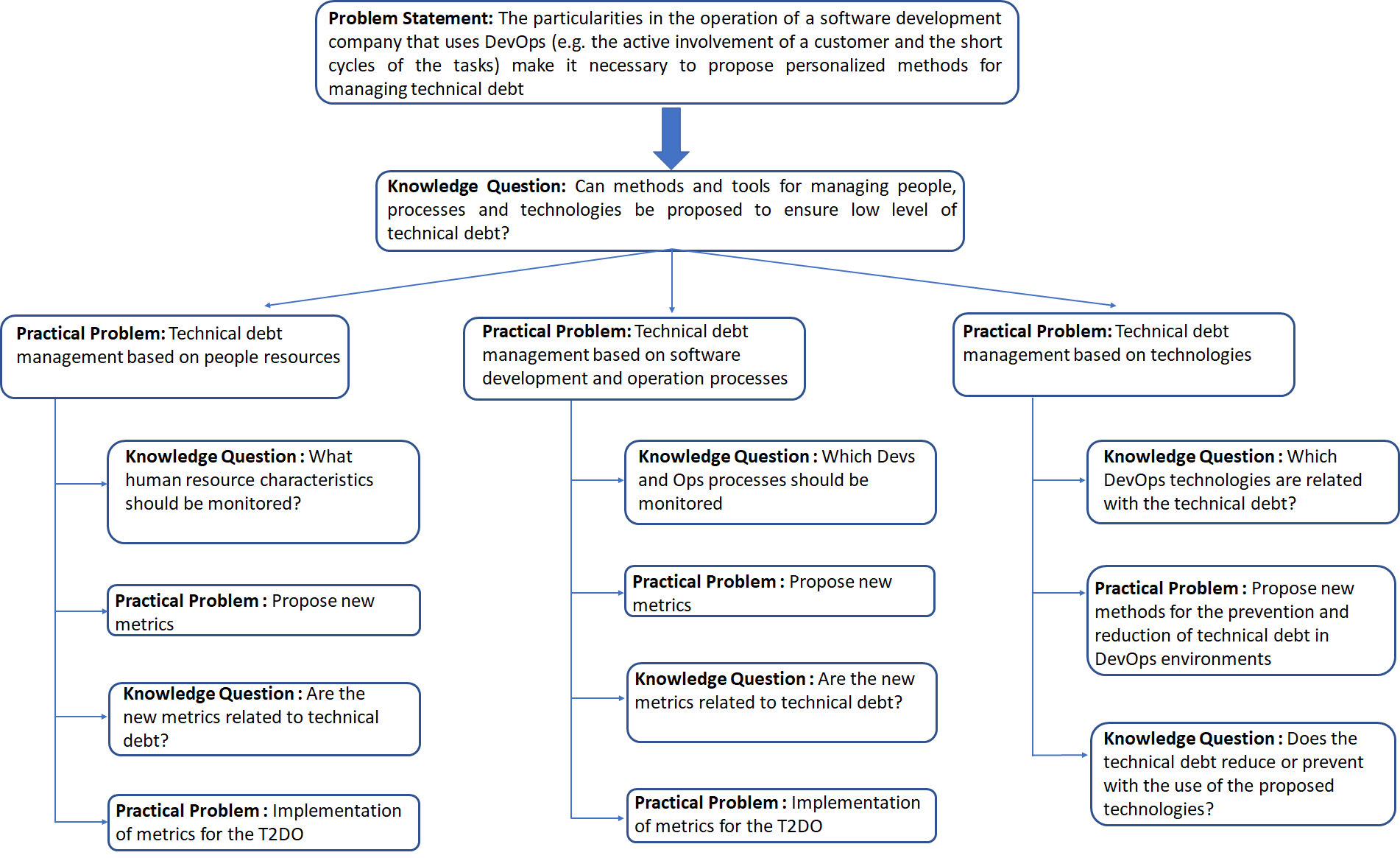
Objectives: Based on the above, the T2DO framework (Technical Debt for DevOps) will provide to the software engineering companies,
methods and tools to assist in monitoring and managing technical debt in DevOps environments.
Method: In order to achieve the above goal, T2DO will propose and provide a series of methods and tools
that will aim at three main axes of evaluation of the software product development and operation processes: people,
processes, and technologies. For each one of the aforementioned axes, T2DO will propose metrics related to the amount of TD
which is accumulated in a software product. In particular, regarding to the "people" axis, metrics will emphasize
the technical and social skills of the people depending on their role in the company (customer, analyst, programmer, etc.).
In addition, regarding to the "process" axis, T2DO will propose: (a) metrics and software quality models for the continuous
monitoring of the product quality at all stages of software development; and (b) process metrics concerning the
application of agile methods. Moreover, regarding the "technologies" axis, T2DO will propose innovative methods that can be applied in
DevOps environments that aim to prevent the accumulation and reduce the existing technical debt.
Evaluation: With respect to the evaluation of T2DO and the methods and tools that have been proposed, a set of empirical studies will be
carried out collaborating with software companies. More specifically, success indicators will be set, and based on
them, we will construct study protocols, which will be used for quantitative and qualitative evaluations.
Expected Impact:The successful completion of the T2DO project will lead to improving the design product quality in DevOps environments. The
companies that will adopt it will have: (a) competitive advantage, since the functionality updates will be available earlier in the market,
and (b) increased capability in project management, as it will maintain a high-level picture of the current situation, as well as it
will provide a number of useful suggestions for improvement in project management. Furthermore, from T2DO, the researcher will also
benefit in various ways, such as: (a) the number of published papers will be increased; and (b) she will implement and target her research on industrial
problems. Finally, the academic institution, in which the research will be performed, will benefit through new industrial collaborations
and the dissemination of knowledge in some cognitive objects.
Mapping Study Statistsics . This tool has been developed and used in the context of various studies. The tool receives as input a csv file that contains all data extracted from the primary studies and produces frequency tables and crosstabs for selected variables of the dataset. Download Tool
Tertiary Study Statistsics . This tool has been developed and used in the context of J1. The tool receives as input a folder containing one file for every secondary study. Within the file the terms and topics identified in each secondary study are recorded. The inter- and intra-topic consistency of terminology are calculated. Download Tool R2EM Calculator. This tool has been developed and used in the context of J3. The tool calculates the ripple effect probability between pairs of requirements. The tool receives various inputs, such as the git repository of the project under study, as well as a file containing the commits and the requirements that have been considered in every commit. Download Tool Instability Calculator. This tool has been developed and used in the context of various studies. The tool receives as input a folder containing the source code of the application under study. The tool calculates the instability and change proneness of classes, as well as the ripple effect on pairs of classes. Download Tool MCPM Calculator. This tool has been developed and used in the context of C10. The tool works in a similar way to Instability Calculator, but calculates the metrics at package level. Download ToolMy Publications
E. M. Arvanitou, A. Ampatzoglou, S. Bibi, A. Chatzigeorgiou and I. Deligiannis, "Applying and Researching DevOps: A Tertiary Study," IEEE Access, May 2022. (.pdf)
A. Ampatzoglou, A. Chatzigeorgiou, E. M. Arvanitou, and S. Bibi, "SDK4ED: A Platform for Technical Debt Management", Journal of Software: Practice and Experience, Willey, 2023. (.pdf)
E. M. Arvanitou, A. Ampatzoglou, A. Chatzigeorgiou, P. Avgeriou, and N. Tsiridis, "A Metric for Quantifying the Ripple Effects among Requirements", Software Quality Journal, Springer, 2023. (.pdf)
P. Smiari, S. Bibi, A. Ampatzoglou, and E. M. Arvanitou, "Refactoring Embedded Software: A Study in Healthcare Domain", Information and Software Technology, Elsevier, February 2022. (.pdf)
M. Krestou, E. M. Arvanitou, A. Ampatzoglou, I. Deligiannis, V. Gerogiannis, "Change Impact Analysis: A Systematic Mapping Study", Journal of Systems and Software, Elsevier, vol. 173, March 2021. (.pdf)
W. E. Wong, N. Mittas, E. M. Arvanitou, Y. Li, "A bibliometric assessment of software engineering themes, scholars and institutions (2013–2020)", Journal of Systems and Software, vol. 180, 2021. (.pdf)
E. M. Arvanitou, A. Ampatzoglou, A. Chatzigeorgiou, J. C. Carver, "Software Engineering Practices for Scientific Software Development: A Systematic Mapping Study", Journal of Systems and Software, Elsevier, vol. 172, February 2021. (.pdf)
A. Ampatzoglou, E. M. Arvanitou, A. Ampatzoglou, P. Avgeriou, A. A. Tsintzira, and A. Chatzigeorgiou, "Architectural Decision-making as a Financial Investment: An Industrial Case Study", Information and Software Technology, Elsevier, vol. 129, January 2021. (.pdf)
A. Ampatzoglou, N. Mittas, A. A. Tsintzira, A. Ampatzoglou, E. M. Arvanitou, A. Chatzigeorgiou, P. Avgeriou, and L. Angelis, "Exploring the Relation between Technical Debt Principal and Interest: An Empirical Approach", Information and Software Technology, Elsevier, vol. 128, December 2020. (.pdf)
D. Karanatsiou, Y. Li, E. M. Arvanitou, N. Misirlis, and E. Wong, "A Bibliometric Assessment of Software Engineering Scholars and Institutions (2010-2017)", Journal of Systems Software, Elsevier, 147 (1), pp. 246-261, 2019. (.pdf)
E. M. Arvanitou, A. Ampatzoglou, A. Chatzigeorgiou, M. Galtser, and P. Avgeriou, "A Mapping Study on Design-Time Quality Attributes and Software Metrics", Journal of Systems and Software, Elsevier, 127(5), pp. 52–77, 2017. (.pdf)
E. M. Arvanitou, A. Ampatzoglou, A. Chatzigeorgiou, and P. Avgeriou, "Software Metrics Fluctuation: A Property for Assisting the Metric Selection Process", Information and Software Technology, Elsevier, 72 (4), pp. 110-124, April 2016. (.pdf)
E. M. Arvanitou, N. Nikolaidis, A. Ampatzoglou, and A. Chatzigeorgiou, "Practitioners’ Perspective on Practices for Preventing Technical Debt Accumulation in Scientific Software Development", 17th International Conference on the Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering (ENASE ‘22), SCITEPRESS, April 2022. (.pdf)
T. Maikantis, A. A. Tsintzira, A. Ampatzoglou, E. M. Arvanitou, A. Chatzigeorgiou, I. Stamelos, S. Bibi, and I. Deligiannis, "Software Architecture Reconstruction via a Genetic Algorithm: Applying the Move Class Refactoring", 24th Pan-Hellenic Conference on Informatics (PCI ‘20), ACM, 20 – 22 November 2020, Greece. (.pdf)
A. A. Tsintzira, E. M. Arvanitou, A. Ampatzoglou, and A. Chatzigeorgiou, "Applying Machine Learning in Technical Debt Management: Future Opportunities and Challenges", 13th International Conference on the Quality of Information and Communications Technology (QUATIC’ 20), Springer, September 2020, Portugal. (.pdf)
E. M. Arvanitou, A. Ampatzoglou, N. Nikolaidis, A. A. Tzintzira, A. Ampatzoglou, and A. Chatzigeorgiou, "Investigating Trade-offs between Portability, Performance and Maintainability in Exascale Systems", 46th Euromicro Conference on Software Engineering and Advanced Applications (SEAA’ 20), IEEE Computer Society, August 2020, Slovenia. (.pdf)
E. M. Arvanitou, A. Ampatzoglou, S. Bibi, A. Chatzigeorgiou, and I. Stamelos, "Monitoring Technical Debt in an Industrial Setting", 23rd International Conference on the Evaluation and Assessment in Software Engineering (EASE' 19), ACM, Copenhagen, Denmark, 14-17 April 2019. (.pdf)
A. Ampatzoglou, A. A. Tsintzira, E. M. Arvanitou, A. Chatzigeorgiou, I. Stamelos, A. Moga, R. Heb, O. Matei, N. Tsiridis, D. Kehagias, "Applying the Single Responsibility Principle in Industry: Modularity Benefits and Trade-offs", 23rd International Conference on the Evaluation and Assessment in Software Engineering (EASE' 19), ACM, Copenhagen, Denmark, 14-17 April 2019. (.pdf)
P. Kouros, T. Chaikalis, E. M. Arvanitou, A. Chatzigeorgiou, A. Ampatzoglou, T. Amanatidis, "JCaliper: Search-Based Technical Debt Management", 34th Symposium on Applied Computing (SAC’ 19), ACM, Limassol, Cyprus, 8-12 April 2019. (.pdf)
S. Charalampidou, E. M. Arvanitou, A. Ampatzoglou, A. Chatzigeorgiou, P. Avgeriou, and I. Stamelos, "Structural Quality Metrics as Indicators of the Long Method Bad Smell: An Empirical Study", 44th Conference on Software Engineering and Advanced Applications (SEAA’ 18), IEEE Computer Society, Prague, Czech Republic, 29-31 August, 2018. (.pdf)
P. Skiada, A. Ampatzoglou, E. M. Arvanitou, A. Chatzigeorgiou, and I. Stamelos, "Exploring the Relationship between Software Modularity and Technical Debt", 44th Conference on Software Engineering and Advanced Applications (SEAA’ 18), IEEE Computer Society, Prague, Czech Republic, 29-31 August, 2018. (.pdf)
E. M. Arvanitou, A. Ampatzoglou, K. Tzouvalidis, A. Chatzigeorgiou, P. Avgeriou, and I. Deligiannis, "Assessing Change Proneness at the Architecture Level: An Empirical Validation", 1st International Workshop on Emerging Trends in Software Design and Architecture (WETSoDA’ 17). IEEE, 2017. (.pdf)
E. M. Arvanitou, A. Ampatzoglou, A. Chatzigeorgiou, and P. Avgeriou, "A Method for Assessing Class Change Proneness", 21st International Conference on the Evaluation and Assessment on Software Engineering (EASE' 17), ACM, Karlskrona, Sweden, 15-16 June 2017. Best Paper Award (.pdf)
S. Charalampidou, A. Ampatzoglou, P. Avgeriou, S. Sencer, E. M. Arvanitou, and I. Stamelos, "A Theoretical Model for Capturing the Impact of Design Patterns on Quality", 32nd ACM Symposium on Applied Computing (SAC’ 17), ACM, Morocco, 3-7 April 2017. (.pdf)
E. M. Arvanitou, A. Ampatzoglou, A. Chatzigeorgiou, and P. Avgeriou, "Introducing a Ripple Effect Measure: A Theoretical and Empirical Validation", 9th International Symposium on Empirical Software Engineering and Measurement (ESEM' 15), IEEE, 22-23 October 2015. (.pdf)
A. Ampatzoglou, A. Kritikos, M. E. Arvanitou, A. Gkortzis, F. Chatziasimidis and I. Stamelos, "An empirical investigation on the impact of design pattern application on computer game defects", 4th MindTREK Conference (MindTREK 2011), ACM, 29-30 September 2011, Tampere, Finland. (.pdf)